Gems, is serving as a decentralized, open-sources, human task crowd sourcing protocol
Let’s get to the bottom of this one
There are a few tasks that the computers can’t complete. However, humans are needed to complete these tasks. In this arena, used as a wide range of large scale distributions. Micro tasks can complete these independently. It does require human judgement.
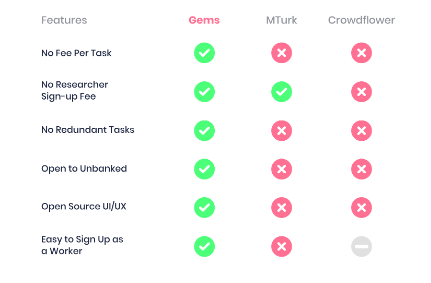
There are huge corporations that pay workers to perform micro tasks online. Apparently, the buzz was generated post Amazon’s Mechanical Turk (MTurk). But there are adversities with the existing centralized marketplaces. There is a high charge per product and the workers eliminate themselves from a potential increase in payment.
Introducing Gems
An open-sourced, human task, crowdsourcing, decentralized protocol that is built on top of the Ethereum blockchain. With this, anyone can access scalable micro task workers. It eliminates the hula over having to verify tasks, trust or payments.
Gems is designed to disincentivize malicious actors and reward fair players. The Gems Protocol is comprised of a staking mechanism to ensure task completion, a trust mechanism to track worker integrity, and a payment system to reduce transaction fees.
How does Gem work?
Gem uses token mechanism, a multi-utility token fuels the Gems protocol.
The first application, Gems Protocol connects the ones who want to get their work done. It enforces the behavior of all participants and doesn’t regulate as a single operator. It removes socioeconomic obstacles that are present in the centralized alternatives.
How does it help?
• Eliminates middleman, who takes a large cut or fee
• Verifies accuracy and efficiency of the results that come from the crowdsourced tasks
• Supplying and building reusable interfaces
• Gets rid of banking infrastructure
• Properly incentivizing and disincentivizing miners and requesters
Other things to know
• Gems Network Overview
It facilitates the extension and efficient operation of the micro task community by allowing organizations to rely and deploy micro task miners. Gems Protocol enables the creation of various platforms that are built on top of the Gems Protocol. Platforms that are created have no intrinsic fee imposed by the Gems Protocol, broaden the scope of the labor supply, and eliminate inefficiencies in the market place. Gems allows any application to utilize efficient online scalable workforce.
• Gems Staking Mechanism
The Gems Staking mechanism provides disincentive for malicious actors, enhancing the efficiency of the Gems Network. Through the Gems Staking mechanism, currently created through Ethereum-based smart contracts, miners, requesters, and verifiers stake tokens on the validity of their work and against the validity of others’ work, providing a palpable disincentive for doing tasks incorrectly.
• Gems Trust Score
The Gems Trust Score is an indicator of how reliable an individual on the network is. By using the individual’s history of completing tasks accurately, efficiently, and consistently, the Gems Trust Score is formed and linked to the network participant’s Ethereum wallet address. With this, it gets easy to create a new address, trust scores and not be easily bootstrapped; miners need a long proven track record to obtain a high score. Miners with very high scores are eligible to verify the work of other members on the network, allowing them to increase the overall accuracy of the system while earning extra money at a higher hourly rate. Unreliable miners will be removed from the network, keeping the quality of work high.
• Gems Platform and Modules
The first application using the protocol is the Gems Platform, a marketplace for matching miners and requesters. The Gems Platform charges no central fee, and utilizing the GEM Token and Gems Protocol, eliminates existing economic inefficiencies. Modules, reusable interfaces for completing specific tasks, are interfaces that are built on top of the Gems Platform.
• Gems Payment System
Transactions on the Ethereum network are not free; they require gas. To allow for micro payments and staking without using gas, the Gems Protocol uses a system of payment channels. Payment channels allow for secure off chain payments without using gas and for the grouping of those payments on the blockchain later. The Gems Payment System will be used by requesters, verifiers, and miners to increase the cost efficiency of the network.
Solutions provided by Gems
The Gems solution increases pay for workers, decreases cost for requesters, enables participation for those unbanked, and introduces a quality management solution, while facilitating the broadening of the network.
• Solution for the problem: Fees
Gems does not charge a centralized fee for transactions on the platform. The only cost on the Gems Platform is gas used on the Ethereum network. Workers and employers will likely share this benefit and return to a fair equilibrium. The end result of having no fees on the platform is a more efficient marketplace for both miners and requesters and the removal of the rent seeking middlemen.
• Solution for the problem: Participation
On the Gems Platform, users do not need to verify their identity to complete tasks. The reason for verifying identity is rooted in preventing malicious actors from abusing the network. The Gems Protocol, and specifically the staking token mechanism, makes the Gems Platform less susceptible to such attacks. In the future, as the Gems Platform branches into areas where information about the miners (geographical, demographical, etc.), may be helpful to requesters, it may allow miners to voluntarily verify to access these specific tasks. Furthermore, if we elect to allow members to voluntarily verify certain information, it can utilize emerging decentralized protocols (e.g. Bloom) to promote an accurate, speedy, and network contributive approach. For those that verify their identity, it may elect to mint Gems for new miners and allow them to hook into an Ethereum faucet to cover transaction costs, to facilitate the broadening of the Gems Network early on.
• Solution for the problem: Payment
Paid on the BlockChain via GEMs. Miners are rewarded for successfully accomplishing a task with GEMs, the reward system of the Gems Platform. Storing GEMs, just like any other ERC20 token, does not involve detailed information about your bank, allowing those who are unbanked and would like to participate to easily do so. Blockchain payments, through the Gems Payment Channels, will reduce necessary transaction fees, which will make transactions on the platform incredibly cost efficient. As blockchain technology gets further disseminated at an increasing pace, being paid on the blockchain will become increasingly attractive. Furthermore, as OTC protocols such as 0x begin to gain momentum, the barrier to transfer between GEMs and other tokens decreases dramatically.
• Solution for the problem: Usability
Open Sourced UI/UX and Modules. The Gems team will work hands-on with early requesters to build reusable UI/UX open source modules to be used on the Gems Platform. Furthermore, the Gems team will build and open source reusable components of modules that will allow the ease of use for anyone to build another module. The Gems team will first build Modules that revolve around AI tasks. Starting with AI tasks, the need for data and specifically scalable annotation services comes from the wide adoption and use of machine learning and specifically deep learning, both subsets of Artificial Intelligence.
What’s in a Gems Protocol?
Miners: Micro task workers
Verifiers: Workers with a high Gems Trust Score who look through miner-completed tasks to verify validity. A verifier replaces many individual miners redoing a single task to verify accuracy
Requesters: Those who want micro task work done
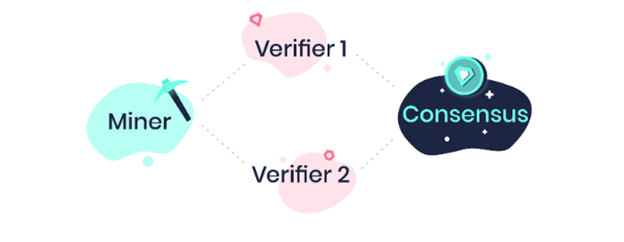
The staking method involves the above
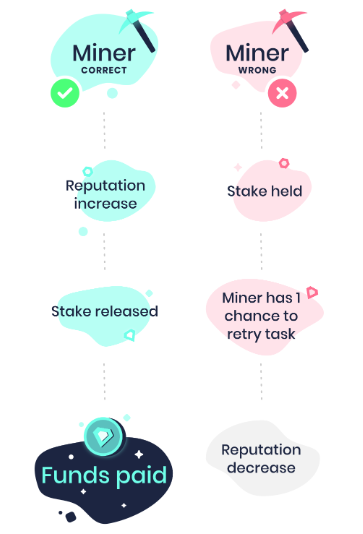
• Miners: Miners stake a token, or a fraction of a token, on a given task. This amount is defined by a variable. If the designated number of verifiers agree the task was completed accurately, the miner is returned, where they’re rewarded. If the verifiers agree the task was completed inaccurately, the miner can either be penalized the stake or redo the task. If the miner successfully redoes the task, he or she is returned, where they’re paid to additional verifiers, the penalty for the miner’s first mistake.
• Verifiers: Verifiers stake a smaller portion of token, on their verification of a task. If other verifiers, or the requesters, overturn the verification, the verifier is penalized. If their work is not overturned, the verifier is returned for any given task.
• Requesters: Requesters stake their total, so they don’t act in bad faith and report successfully completed tasks as incorrect. If requesters deny a task as being correct, that same task will be given again to other miners/verifiers, and the requesters funds will still be locked up, meaning that there is no clear incentive for a requester to be a malicious actor.
Gems Community Program
The Gems Community Program is the way to secure a spot in the Gems Pre-Sale/Token Launch.
• Join the Gems Telegram. Demonstrate that you will use the Gems Protocol and contribute to its ecosystem.
• Help in growing: Share the Gems mission with others who can use the Gems Protocol. The possibilities are endless —but here are a few:
a) Invite people to the Gems Telegram
b) Write a blog post
c) Make a YouTube video
d) Drive constructive discussions in the Telegram and beyond
e) Your own innovative idea
Why choose Gems
Gems provides economic efficiency to network participants, properly incentivizes miners to accomplish tasks, disincentivizes malicious actors, opens access to those who are unbanked, and opens access to the labor supply of micro task workers without intrinsic network fees.
See how it’s better than the existing ones