Given the recent rise in ransomware there has been a spark of interest in some people into to what are referred to as "cryptocurrencies". I am going to discuss what they are, what part they play in ransomware attacks and the pro and cons of these things.
First, let's take a look at the biggest major currency to date: Bitcoin. According to Wikipedia: "Bitcoin was created by Satoshi Nakamoto, who published the invention on 31 October 2008 to a cryptography mailing list in a research paper called "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System". Nakamoto implemented bitcoin as open source code and released in January 2009" Bitcoin is a decentralised currency, meaning it doesn't come from one place alone. In normal currency, a Mint is responsible for the creation of bills and coins. In Bitcoin, no one person or organisation is responsible for the creation of Bitcoins.
What exactly is a Bitcoin? A Bitcoin is essentially a unit of currency, cryptocurrency, similar to the likes of a pound or a dollar. So then, what happens in the process of creating a Bitcoin? Well, Bitcoins are created via the process of Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin mining is not a physical act, but rather the result of the algorithms. Here is the process of mining in a convenient cartoon:
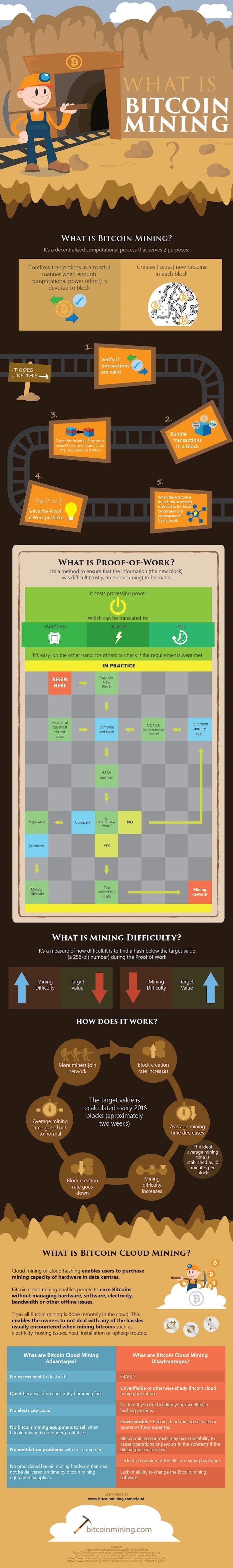
Bitcoin mining can be done by anyone but it is computer resource intensive. That means that once you dedicate a computer to bitcoin mining it is pretty much useless for anything else. Therefore people often build computer systems with the intention of using them solely for mining. They are often very basic machines which have a strong processor in them and a lot of cooling. There is a market of pre-made Bitcoin machines which you can buy. The cool thing about this is that if you buy one of these machines they can pay themselves off.
[caption width="402" id="attachment_1955" align="aligncenter"] This cartoon pretty much sums up the "difficulty" of bitcoin mining.[/caption]
This cartoon pretty much sums up the "difficulty" of bitcoin mining.[/caption]
So, you now know what Bitcoin is and the process of creating Bitcoins. However, we still haven't answered the first question, which was "What is a crypocurrency?" and to find the answer to that we will take a look at what makes Bitcoin one.
All Bitcoin transactions are anonymous, and are view able by everyone, however transactions are encrypted. The blockchain is stored on every computer in the mine, so if one computer goes offline no transactions are lost. This is part of the decentralised system that is Bitcoin. The encrypted transactions are what make Bitcoin a crypocurrency, and are what helps make new Bitcoins as hashes are calculated for every transaction. While transactions are encrypted, they could quite easily be traced back to you if someone knows enough information because all actions are public. However, Bitcoin addresses are not themselves linked to a person or entity. That's why Bitcoin is often called pseudonymous or pseudo-anonymous. Transactions are also very quickly lost in the list and so trying to find a transaction is extremely difficult. Similarly with real (physical) money, it would be very hard to get the money you traded back unless the dealer decides to refund you and this is the same sort thing that happens in Bitcoin.
It could be said that crypocurrencies are an part of the recent rise in ransomware. If we take a look at WannaCry, the message asks for Bitcoin and promises to decrypt your files if you pay up. If it wasn't for Bitcoin then this would not have been so bad as I don't think the author would have seen the point in releasing the malware. Classically, malware would have been out simply to cause havoc, but now they are asking for money and this is all because transactions can easily be completed by Bitcoins which cannot be refunded. It takes little effort of the authors to easily set up a Bitcoin wallet but it would be harder for them to set up a bank account which could ultimately be traced back to them. Basically the hackers will use Bitcoin as it cannot be easily traced in the way standard bank transactions could be traced.
[caption width="642" id="attachment_2020" align="aligncenter"] As you can see, the WannaCry message clearly says that it accepts Bitcoins. This transaction would not have been possible without this kind of currency and so because all the author want is money Bitcoin is perfect for this.[/caption]
As you can see, the WannaCry message clearly says that it accepts Bitcoins. This transaction would not have been possible without this kind of currency and so because all the author want is money Bitcoin is perfect for this.[/caption]
So, here we can see that people are trying to profit from Bitcoin and scaring others into giving Bitcoins. Previously, ransonware was a small part of the malware market. Before malware usually consisted of destructive viruses, trojans, keyloggers and the like. However now that the malware authors see a way to profit from their activities then malware will be on the rise. Of course, you absolutely should not pay the ransom. Doing so will only perpetuate the ransomware industry. You won't get your files back. If your smart you can avoid damage from these things by having an offline backup, such as keeping a copy of your important documents stored on a hard disk that is kept disconnected from your computer.
Let's discuss the pros and cons of Bitcoin (using it as an example for all cryptocurrency):
Cons
- Bitcoin has a major design flaw. The creator designed it to almost self destruct when it reaches a certain number of bitcoins. When this number is reached, Bitcoin creation will cease and who knows what after that. That means there is a finite amount of coins in the world.
- Another problem is the decentralisation of Bitcoin. At the time of writing this, Bitcoin is going through an update. That means that soon two versions of bitcoin will be in existence, and the two will not be compatible with each other. Another problem is that it is not regulated so anyone can make bitcoins and use the for any purpose. This may be good for some things, but what about that person who is using his bitcoins on the dark Web to do evil things?
- Comparing the pricing of objects in bitcoin to real money, it can be hard to ask for bitcoin. For example, if you are buying something with bitcoin the price could be some crazy number like BTC 0.58472809. This is horribly inefficient.
- While transitions can be tracked, they can be hard to trace back to you.
- Can be useful for online purchases
This article was abandoned near the end of writing but I decided to release it because I didn't want it to go to waste
This was originally posted on my blog at WordPress