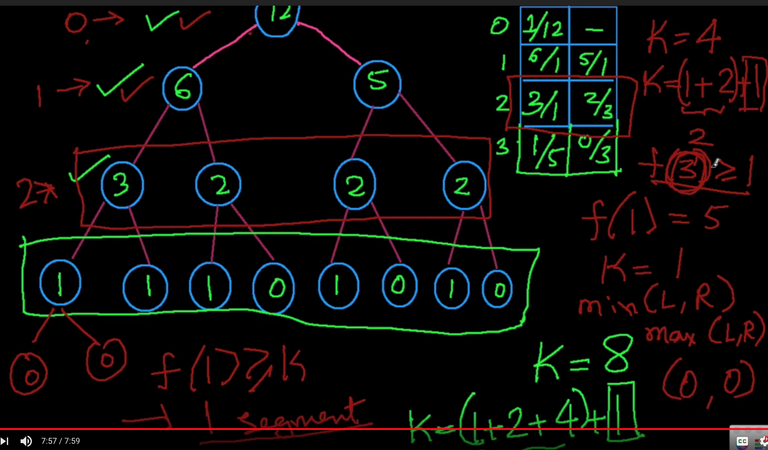
f(x, y, k, a, b)- first input
f(1, 0, k, n, n+1) 1+0 >= k {return b}k -= x+ycreate map<LL,LL>mand adda--; m[a/2]+=x; m[a-a/2]+=x// offset of left & right respectivelyvector<pair<LL,LL>> v(m.begin(), m.end())- return either
aorbas t t--//minus the location of last item it self and then usemax, mintoa/2anda-a/2respectively
Core:
m[(n-1)/2] += 1
m[n-1 - (n-1)/2] += 1
n[n/2] += 0
n[n/2] += 0

- Find any longest subsequence of consecutive empty stalls
- Choose the middle stalls

A great explanations by using tree n/2 & (n-1)/2