
Hello my steemit friends i will share you some help that might encounter you today or later in your computer that can break your head and your files. Please vote me and subscribe i will provide more tips and helpful ideas.
Before we start we need to know what are different computer virus.
Know what damage a virus could do to you

We loathe virus, undoubtedly. Do you know how viruses can damage your computer exactly? There are many types of viruses, and they behave in many differentiated ways. To sum up, a computer virus is simply a type of program that causes your computer to act in an undesirable way. It can be dangerous, to drag your computer down, erase very important files, or gives hackers access to your personal information...
Viruses are nuisance, unfortunately, it seems unlikely to avoid it. Some viruses like Locky virus and CryptoLocker, also known as ransomware, delete computer files, encrypt them, even change the file extension to .locky or .encypt, while some virus hide files, making users find nowhere to unhide them. f you happen to be a victim who's looking for .locky file recovery and .crypt file recovery, then click the links.
Different Type of Virus
- Boot Sector Virus
From a user perspective, boot sector viruses are some of the most dangerous. Because they infect the master boot record, they are notoriously difficult to remove, often requiring a full system format. This is especially true if the virus has encrypted the boot sector or excessively damaged the code.
- Direct Action Virus
A direct action virus is one of the two main types of file infector viruses (the other being a resident virus). The virus is considered “non-resident”; it doesn’t install itself or remain hidden in your computer’s memory.
It works by attaching itself to a particular type of file (typically EXE or COM files). When someone executes the file, it springs into life, looking for other similar files in the directory for it to spread to.
- Resident Virus
Resident viruses are the other primary type of file infectors. Unlike direct action viruses, they install themselves on a computer. It allows them to work even when the original source of the infection has been eradicated. As such, experts consider them to be more dangerous than their direct action cousin.
Depending on the programming of the virus, they can be tricky to spot and even trickier to remove. You can split resident viruses into two areas; fast infectors and slow infectors. Fast infectors cause as much damage as quickly as possible and are thus easier to spot; slow infectors are harder to recognize because their symptoms develop slowly.
- Multipartite Virus
While some viruses are happy to spread via one method or deliver a single payload, Multipartite viruses want it all. A virus of this type may spread in multiple ways, and it may take different actions on an infected computer depending on variables, such as the operating system installed or the existence of certain files.
They can simultaneously infect both the boot sector and executable files, allowing them to act quickly and spread rapidly.
The two-pronged attack makes them tough to remove. Even if you clean a machine’s program files, if the virus remains in the boot sector, it will immediately reproduce once you turn on the computer again.
- Polymorphic Virus
According to Symantec, polymorphic viruses are one of the most difficult to detect for an anti-virus program. It claims anti-virus firms need to “spend days or months creating the detection routines needed to catch a single polymorphic”.
But why are they so hard to protect against? The clue is in the name. Anti-virus software can only blacklist one variant of a virus – but a polymorphic virus changes its signature (binary pattern) every time it replicates. To an anti-virus program, it looks like an entirely different piece of software, and can, therefore, elude the blacklist.
- Overwrite Virus
To an end-user, an overwrite virus is one of the most frustrating, even if it’s not particularly dangerous for your system as a whole.
That’s because it will delete the contents of any file which it infects; the only way to remove the virus is to delete the file, and consequently, lose its contents. It can infect both standalone files and entire pieces of software.
- Spacefiller Virus
Also known as “Cavity Viruses”, spacefiller viruses are more intelligent than most of their counterparts. A typical modus operandi for a virus is to simply attach itself to a file, but spacefillers try to get into the empty space which can sometimes be found within the file itself.
This method allows it to infect a program without damaging the code or increasing its size, thus enabling it to bypass the need for the stealthy anti-detection techniques other viruses rely on.
Luckily, this type of virus is relatively rare, though the growth of Windows Portable Executable files is giving them a new lease of life.
This time i will show you a sample program of computer virus.
Toggle your friend's Caps Lock button simultaneously:
Type :
Set wshShell =wscript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
do
wscript.sleep 100
wshshell.sendkeys "{CAPSLOCK}"
loop
Save it as "Anything.VBS" and send it.
The only purpose of this code is for educational purpose only.
Now lets talk how to remove virus even without antivirus.
In this page, we're going to offer you solutions to remove viruses from your USB drive, memory card, in fact, any drive in a Windows 10 computer using CMD. In order to remove a virus using CMD, we will use a famous CMD command called 'attrib' command. So first, we'd better have some understanding about the commands we're supposed to use.
Here are the basic attributes of the 'attrib' command which we will use later:
R – R represents the "Read-only" attribute of a file or folder. Read-only means the file cannot be written or executed.
H – H stands for the "Hidden" attribute.
A – Similarily, A stands for "Archiving" which prepares a file for archiving.
S – S attribute changes the selected files or folders into a system file from a user file by assigning the "System" attribute to that particular file.
"attrib" Syntax:
ATTRIB [+ attribute | – attribute] [pathname] [/S [/D]]
In the above command, let's see what the different parameters and switches are:
'+ / –': To enact or to cancel the specified attribute.
'attribute': As explained above.
'/S': Searching throughout the entire path including subfolders.
'/D': Include any process folder.
'pathname': Path where the target file or folder is located.
Here is the proper syntax for attrib command:
ATTRIB [+R | -R] [+A | -A ] [+S | -S] [+H | -H] [+I | -I] [drive:][path][filename] [/S [/D] [/L]]
Just give you an example. I am going to transfer an 'autorun.inf' virus from my USB drive to my D: drive and delete that virus from my D: drive.
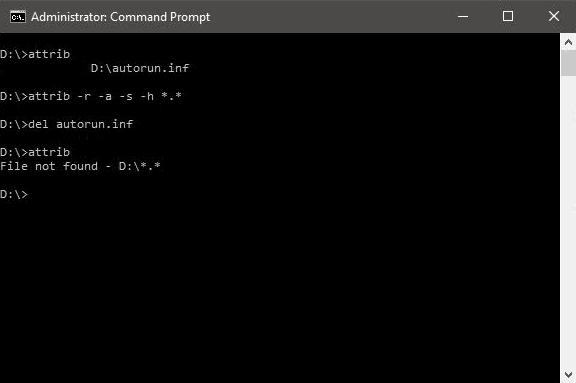
Step 1. Open Command Prompt from search and run as an administrator.
Step 2. Type D: and press Enter.
Step 3. Type attrib and press Enter. You'll see autorun.inf virus listed.
Step 4. To remove virus using CMD, type into your command prompt attrib -r -a -s -h . and press Enter. This will remove the Read Only, Archive, System and hidden file attribute from all the files. (. for all the files with all different types of file extensions).
Step 5. Type del autorun.inf and enter, to delete the files.
If you are infected by other viruses, replace autorun.inf with other virus extenstion such as *.ink or *.exe so to respectively delete those suspicious files.
Thank you all my steemit brothers and sisters please vote me and subscribe.