Curious Fact
Continuity Equation
A fluid that is in motion can change its speed along its trajectory, for example: In a river we can observe how water advances much slower in wide sectors than in those sectors that are narrow or shallow. This is due to the fact that the fluid advances with greater speed in the areas where the area of the surface is smaller.
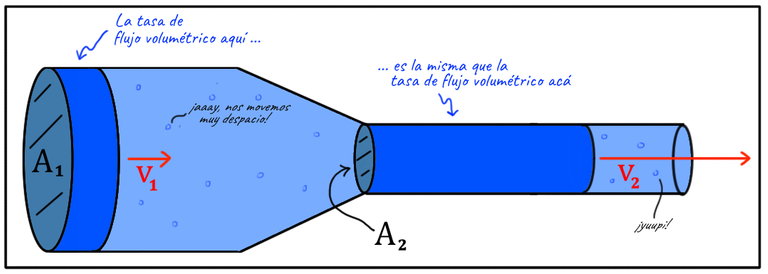
We can mathematically express this behavior through the continuity equation, which states that every flow Q = constant at any point of a channel or pipe. Which means that Q1 = Q2
If we substitute Q = V * A where:
V = Volume
A = Area of transversal section
It remains expressed then:
A1V1=A2V2
This expression is known as the Continuity Equation for incompressible fluids. Ideal to calculate the speed of a fluid in any part of the pipe where it is located.