The blockchain is essentially a decentralized distributed ledger database. It is itself a string of blocks generated using cryptography, each block containing information validly validated for many transactions on the Bitcoin network. This is the definition of a blockchain, so to understand the blockchain step by step, we need to know one thing at a time.
To center
First consider a centralized process. You want to buy a cell phone on a treasure, the transaction process is: You will call the money Alipay - Alipay receipt after the notification to the seller delivery - the seller shipped - you confirm the receipt - Alipay hit the seller to the money.
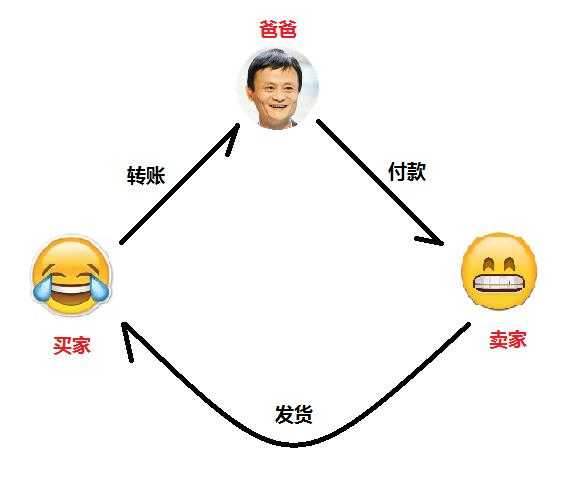
Figure 1: Centralized centralized trading model
In this process, although you are dealing with the seller, but the deal also involves you and the seller's third party, Alipay, you and the seller's transactions are all around Alipay. Therefore, if the Alipay system out of the question will result in the failure of the transaction. And although you simply bought a cell phone, both you and the seller have to provide extra information to third parties. Therefore, consider the extreme situation, if Alipay ran or took the money does not recognize your transaction or Alipay city where open G20 everyone (?), Then you are tragedy.
Decentralized processing is much simpler, you only have to exchange money and cell phones with the seller, and then both sides claim they have completed the deal.
It can be seen that in some specific cases decentralization is easier and less worrying about the leakage of information that has nothing to do with the transaction.
In fact, if we only consider the transaction of two people and can not fully demonstrate the benefits of decentralization, imagine that if there are tens of thousands of transactions going on, the centralized approach will save a lot of resources and make the entire transaction autonomous and simple And eliminates the risk of being controlled by a centralized agent.
Decentralization is a subversive feature of blockchain technology, which realizes a kind of point-to-point direct interaction without centering proxies, which makes it possible to exchange information efficiently with large-scale and decentralized agents.!
Of course, the above example has a big potential problem: how to ensure the accuracy and validity of each transaction without an authoritative centralized proxy? For example: Without the authority of the central agent, Zhang Sanmou borrowed 100 dollars a day, but do not repay the money do not recognize how to do? Here comes the other features of the blockchain.
We are sharing next.!
Thank you for posting