Cyber•Fund is introducing a series of publications that provide an overview of some of the best speaker topics we’ve hosted at our meetups. Valery Litvin — cyber•Fund’s CTO — unveiled the blockchain browser at cyber•Fund’s Blockchain Fairytales conference in Minsk, Belarus. In his opinion “cyber•Search will serve to further develop blockchain infrastructure by creating a single registry for all registries that exist.”
Hard and Soft Problems
In the blockchain field there are two classifications of problems: hard and soft. Vitalik Buterin first defined hard problems as economic finality, parallelism, speed and decentralization/ cost privacy. At cyber•Fund, the development team began to consider the whole blockchain industry and the applications ecosystem working with it. As a result they have defined a set of soft problems; another class of tasks related to search, analytics, accounting and interaction. The cyber•Search team works on the development of blockchain infrastructure and addressing the specific soft problem of search.
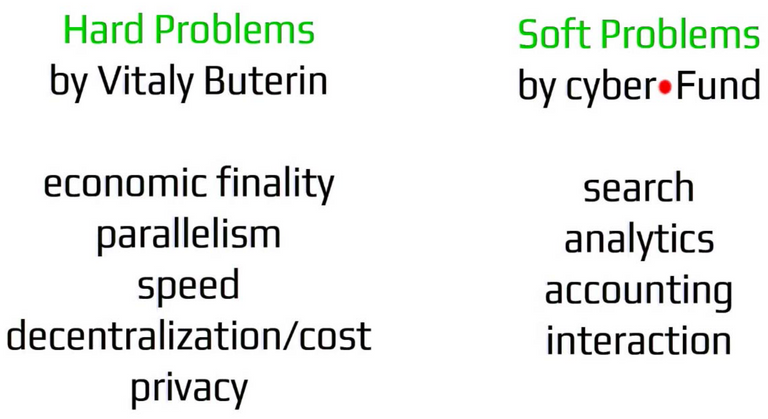
Here is a quick breakdown of the components of soft problems:
Search
- Across blockchains
- Across smart contracts
- Blockchain Indexing
Analytics
- Blockchain specific
- Centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency markets
Accounting
- Tokens and portfolio accounting
- Performance accounting
- Fund tools
Interaction
- Among Blockchains
Note that interaction is the least salient problem, but that does not mean it is any less important. The soft problem of interaction can be combated by having a lot of different tokens, in which case you encounter the lack of ability to work with all of them concurrently. Multi-currency wallets currently exist, but there is no open source code software for these wallets.
Problem Solving
In order to solve these problems we first need to focus on search tools and the indexation of blockchains. At this particular moment the cyber•Search team is developing the blockchain browser that already works with four blockchain networks and can index blocks, transactions, addresses, balances and mempool.

The blockchain browser was already released, but there is still a lot of work to do. The team is working with documentation so that every developer can add indexing of any blockchain.
Their work priorities:
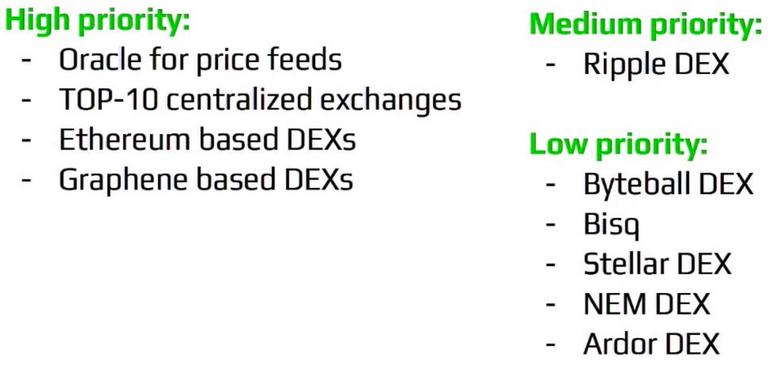
They are also focusing on centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency markets. They currently work with five centralized exchanges and one DEX. The team plans to create an open source tool that allows the aggregation of data from every exchange in order to receive trades, order books, count tickets and make this information public. The unique feature of this open source tool will be the implementation of its’ combined order book.

Stack and Chaingear
Here is a list of what their stack includes:
JVM (Kotlin)
Kafka
ElasticSearch
Cassandra
Nginx/ Docker
Kubernetes
They have dubbed their stack as cybernode, and furthermore everyone can use it as SDK, Backend and Infrastructure.
Chaingear is cyber•Fund’s first analysis product that includes meta information about all blockchains, tokens and crypto-projects combined by common methodology. They plan to transform Chaingear and move it to Ethereum smart contracts in order to develop an open sourced registry of registries under the MIT license.

By far, the most exciting project that the cyber•Search team has in the works is the creation of a decentralized Google search engine. You might wonder how they possibly produce a better Google, or what a better Google would even look like:
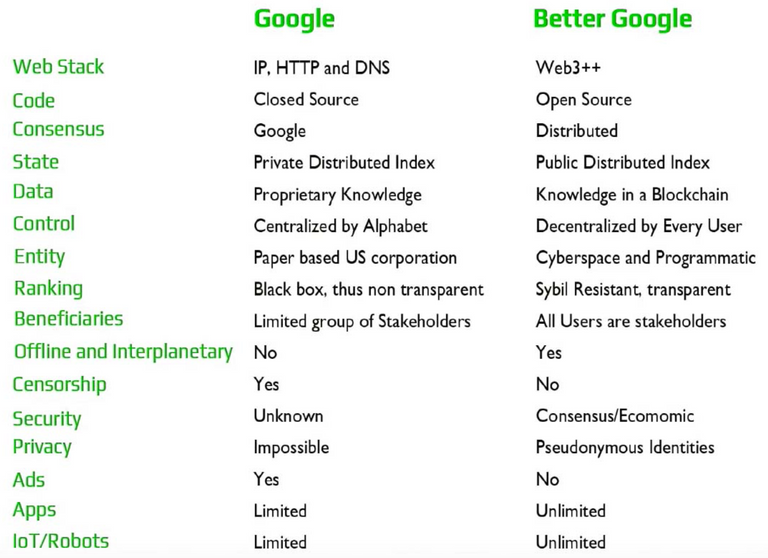
Check out all of cyber•Fund's open source solutions here.
For information please contact: pr@cyberfund.io