The Cypherpunks mailing list reached 2,000 subscribers.
Satoshi Nakamoto sent the Bitcoin White Paper to this group of activists.
The Bitcoin story begins in 2008, when Satoshi Nakamoto publishes the cryptocurrency white paper for the first time, sending it to a small group of specialists in computer science and cryptography, focused on privacy and defense. That group was made up of the senders of the mailing list of the cypherpunk movement.
Although this list was established in 1992, the ideas and the group as such had already been developing since the 1980s, especially driven by the work of David Chaum. We speak of one of the first specialists to worry about the privacy of financial transactions and develop a digital system to solve these problems. If there is a Bitcoin grandfather, Chaum fits perfect.
THE CYPHERPUNKS WRITE CODE
The cypherpunk movement raised the banner of privacy, especially in the face of the threat of control and censorship by governments and central authorities over technological development, information and the exchange of value.
In this case, privacy could be understood as the legitimate right of every citizen of the world to reveal only the information that he or she wants. This is a power for these activists and could be summarized in the following sentence of Eric Hughes' Cypherpunk Manifesto
Privacy is the power to selectively reveal oneself to the world.
Cypherpunk Manifesto
Now, it is not just a privacy. This issue is particularly relevant in the context of open societies, of freedoms, but in the middle of the digital age. Thus, members of the cypherpunk movement not only discussed and theorized about the topic, but also developed software to help achieve this goal.
Most of the members of the mailing list were prominent researchers and specialists in computer science and associated sciences. And in addition to privacy issues, they discussed the problems associated with government monitoring, corporate control of information, among others.
Cryptography deserves a special mention. Recall that at that time, the civilian use of this technology was prohibited, and the US government qualified it as "ammunition" for export purposes, so that its commercial expansion was not possible.
The US government tried to control this type of development and even the code of the Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), was published in a paper book to circumvent these impositions.
The mailing list was created by Timothy May, Eric Hughes and John Gilmore. The mailing list was called CoderPunks, and it was originally hosted on the Gilmore toad.com server.
WHO?
Some of the participants on the list maintained anonymity, however, others are publicly known, being artisans or active participants in the creation of software tools to improve privacy.
Some of the first cypherpunks:
Julian Assange, founder of WikiLeaks.
Bram Cohen, creator of BitTorrent.
Jacob Appelbaum, developer of Tor.
-Philip Zimmermann, creator of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP).
-Zooko Wilcox-O'Hearn, developer at DigiCash and founder of Zcash.
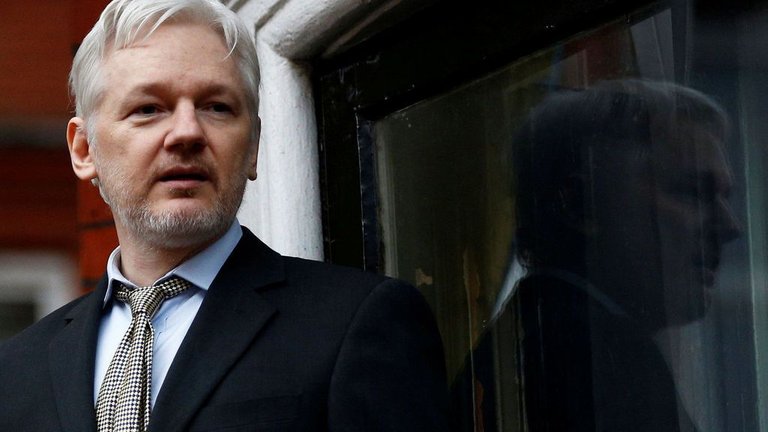

Assange is one of the most popular cypherpunks. Source: Reuters.
However, as far as its ancestry for Bitcoin (beyond the own Nakamoto) and its happening it is possible to emphasize Adam Back, inventor of Hashcash; Hal Finney, important developer of the PGP system and creator of the Reusable Work Test; Wei Dai, creator of b-money, one of Bitcoin's most prolific antecedents; and Nick Szabo, creator of Bit Gold, an important forerunner of Bitcoin's architecture.
BITCOIN AS A SYNTHESIS
If you look closely, Bitcoin is a synthesis of ideas and projects that did not work or did it only partially. These last cypherpunks are important in this regard. Its influence or relationship with Bitcoin, its objective and design, is clear.
As for Back, in addition to a mention in the Bitcoin White Paper itself, the cryptocurrency protocol inherited its underlying technology, ie the Work Test. And is that while Hashcash was designed to enhance anti-spam systems, the operation of the Work Test it uses has its counterpart in the design of the bitcoin mining algorithm.
The invention of Back has not been patented and is an open source technology, which has been implemented for protection systems against DDoS attacks.
Wei Dai's b-money could be considered a Bitcoin draft. The operation of one and the other have many similarities. Thus, and despite the fact that Dai himself has assured that Nakamoto would not have read his work, like Bitcoin, b-money required a specific amount of computational work; this work had to be verified by the users who update a public ledger.
In addition, those who participate in the Work Test of the system receive a reward for their activity; and the exchange of funds is done thanks to this collective accounting and is authenticated with cryptographic hashes. However, unlike Bitcoin, b-money never started.
Nick Szabo created Bit Gold as a value-exchange system resistant to third-party dependence. He proposed an interesting solution to the potential Byzantine failures in the consensus of the network and against the possibility of carrying out the double expense of the accounting unit of the network.
To avoid the double spending of the coins, a mathematical problem had to be solved. The problems already solved would be sent to the public registry, and each solution would become part of the next problem to be solved, creating an increasing chain of new properties. This aspect of the system provided a way for the network to verify and mark new currencies; a clear predecessor of Bitcoin timestamp server.
In the case of Finney, not only its collaboration with the development of a fully functional Reusable Work Test system before Bitcoin, but especially its direct participation in the early days of Bitcoin make it an important reference.
In addition to being one of Nakamoto's most active interlocutors, Finney was one of the first to download and run the first version of the Bitcoin client from Nakamoto. In addition, he is the first recipient of a transaction in the network, after Satoshi himself sent him 10 BTC.
De Wei, Szabo and Dai have been told that they could be Satoshi Nakamoto. However, each one has denied it, leaving the anonymity of the Bitcoin creator intact.
BITCOIN: A CYPHERPUNK PRODUCT
In a way, Bitcoin is a cypherpunk product. Although it did not have a particularly effusive reception, it is not only a synthesis of several projects inspired by this movement, it is also the realization of several of its ideals.
Thus, despite its pseudo-anonymity, Bitcoin complies with the basic principles of privacy and its protocol can reach higher levels of fungibility, so that transactions can be truly anonymous, despite the analysis of the chain of blocks. "An anonymous system allows individuals to reveal their identity when desired and only when desired; this is the essence of privacy, "reads the Cypherpunk Manifesto.
Privacy has always been a search for partnerships, according to Hughes. Search that can be crystallized with the implementation of new technologies, since "the technologies of the past did not allow a strong privacy". In this case, cryptography is a fundamental element, necessary for the development of truly private payment, communication and exchange solutions.
In addition, its decentralized and censorship-resistant operation provides an important network for the exchange of value and information, which does not depend on the will of an institution or regulatory entity. The users and their own value relationships within the network are independent to the will of any group, this without directly compromising the identity and critical information.
It is no accident that Satoshi Nakamoto has decided to send the Bitcoin White Paper to the email list of
It is no coincidence that Satoshi Nakamoto has decided to send the Bitcoin White Paper to the Cypherpunks mailing list. The philosophy of this movement and the possible motivations behind the creation of Bitcoin adjoin.
Although Bitcoin could be described as an apolitical tool, because the protocol and its operation are completely independent of the interests and opinions of its users, its creation was due to a particular context, for which Nakamoto proposed a solution: an exchange network of value (with potentially private transactions), decentralized and global in scope, woven as the mosaic of several projects that the cypherpunks had matured for years.
Wow very detailed article. Funny it took so long before it started to get value to the world. Quality content man!
Thank you, brother, how are you? Impure me for continuing to improve @semtroneum