What is Classical Architecture
Classical architecture is a building style and designing technique that refers to the classical period of Greece, as used in ancient Greece in the Hellenistic and Roman Empire periods. In the history of architecture, Classical Architecture is also later composed of a more modern style of derivative style derived from Greece.
The predicate of the word 'classical' is given to a work of architecture that has an immortality value in addition to its quality and value. Classical architecture refers to the early period of the development of the flow of historical and cultural studies of Greece and Rome, which later became the influence of the next epochs. In classical architecture, his work centers on sculptural works in colossal form, with functions as visualizations of religion, scripture, and other beliefs, even as a means of religious ritual.
Greece has a typology of hilly territory that separates some tribes that after the tribe began to be organized formed the policy (city state) and run the government by way of democracy. This hilly typology makes Greece rich in stone, so many building materials using stone.
Nashville Parthenon, USA
image source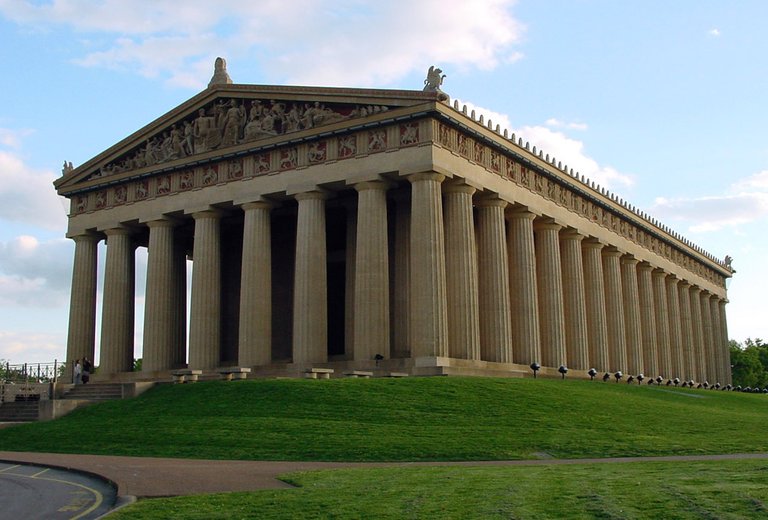
Classic architecture is an expression and description of the course of European architectural history that specifically refers to the works of high value and first class architecture. It is so called because these works have strict rules or guidelines and careful consideration as the basis for thinking in creating the work.
Classical Architectural Character
Classic architecture gives the impression of elegance and luxury. characteristic of classical architecture is the use of pillars, ornaments, and profiles that emerged during the ancient Roman or Greek empire. The classical style building has a size that exceeds the needs of its function and has a symmetrical building composition with a regular window layout.
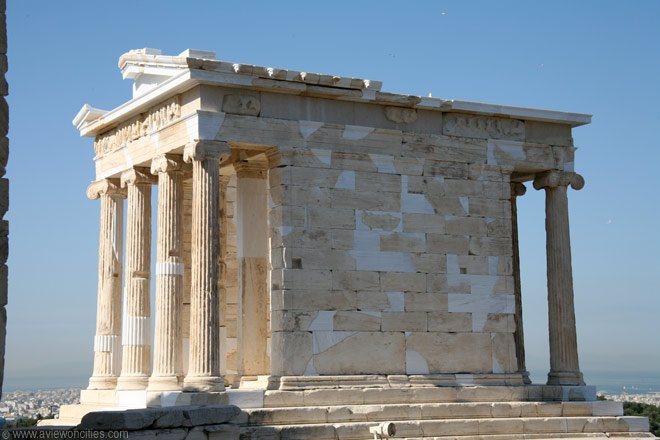
The Acropolis, Athens, Greece.
image source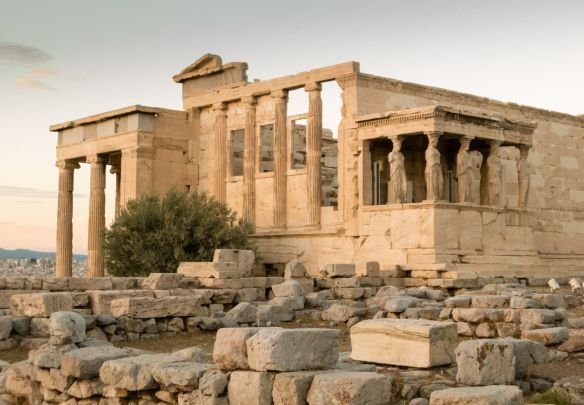
When we think of classical architecture, we generally think of a building made of wood, stone, etc. In some examples of buildings, this is true. However, the classical architecture also has a lot of modern breath and elaborate building design, for example on the roof, pole, even stone or marble structures are made with the perfect detail.
Classical Architectural Functions
Classic architecture is built with three functions, first as a residence, secondly as a place of worship for God or a house of worship, and the third as a gathering place like a town hall. For this second and third reason, buildings with classic style are made as detailed and as beautiful as possible by giving intricate ornaments ornaments.
Characteristics of Classical Architecture
The hallmarks of classical architecture are as follows :
- It has a lot of ornaments or decorations almost in every corner of the building.
*The use of columns and beams (entablature) as the main element. - Usually a large and magnificent building with a long workmanship time.
- Utilizing the effects of eye distortion to create the grandeur and beauty of the main buildings.
- The main ingredients use ingredients that are directly taken from nature.
- Every building on Ancient Greek architecture is an integral part of the entire structure so that its remains (though imperfect) can be reconstructed into an actual building.
Example of Classical Architecture
One of the most famous classical-style buildings is the Parthenon. Parthenon is a temple to the goddess Athena built at the highest hilltop in Athens, which is in Acropolis. After the Dark Ages (Dark Ages), the city of Athens was no longer governed by the king. Instead they apply the oligarchy system. Thus, the Acropolis was no longer the residence of the king, but became a shrine to the goddess Athena, and the Athenians built a temple for the goddess there. The city council of Athens hired two prominent architects, Kallikrates and Iktinus, as well as the famous sculptor, Pheidias, to build the Parthenon. The entire building is made of marble while displaying the latest architectural style with a larger size.
Parthenon architects want to build the best temple in Greece. When most of the Greek temples had six poles on the front, the Parthenon had eight columns. Other Greek temples are decorated by friz (metallic stone only) or methane (individually decorated stone panels) only, while the Parthenon also has friz and metope.
Another example of a classic Greek building is the Nike Athena temple. Nike Temple, is the smallest temple in the Acropolis. But for the citizens of Athens, Nike is considered as a lucky bearer for the city of Athens. The Nike Athena Temple has a tetrastyle (four columns) with a colonnaded foyer on both the front and back faqs (amphiprostyle) designed by the architect Kallikrates. This building was built on the remains of an ancient Athena temple in the sixth century that was destroyed by the Persians in 480 BC. The temple was built of white pentelic marble. Inside this temple there is a statue of Nike, which means victory. The maker removes the Nike wing that is supposed to exist so that the victory does not go away from Greece. This is what causes this statue is better known as Nike Apteros.
A Brief History of Classical Architecture
When people think of classical architecture, they generally think of buildings made of wood, stone, and others. In some cases, this is true, but the classical architecture also has many modern breaths and elaborate building designs. For example, roofs, poles, even structures of stone or marble are made with perfect detail.
Colosseum, Rome
image source
Classical Architectural Style emerged along with the commencement of the formal writing civilization. Not yet discovered specifically when this era begins or ends. However, this type of style is often found in continental Europe. For some reason, this type of architecture is built with three purposes: as a shelter (the function of a dwelling house, as a place of worship of God (the function of the house of worship) and a gathering place (town hall, etc.) For the second and third reasons this building is made as detailed as possible and as beautiful as possible by giving a complicated ornament.
As time passes, the building becomes more complicated and more detailed. Some civilizations that grew out of rocks and mud helped enrich various forms of Classical Architecture, such as temples and Egyptian tombs.
Classical Architectural Theory
Classical architecture is an expression and description of the course of architectural history in Europe that specifically refers to the works of high-value and "first class" architecture. It is so called because these works exhibit strict rules / guidelines and careful considerations as the basis for thinking and creating the work. The time span of this age is from the first century up to the 14th century with the wind blow romantism (before European society entered the Renaissance until the message and movement of strong Rationalism).
The "Classical" word predicate is given to an architectural work that is inherently contained in immortality as well as its quality and value. Classical architectural theory is thus an architectural realization that is based on and animated by the ideas and ideals of the Theory of Vitruvius especially in a period of time after Vitruvius himself died.
The Parthenon building in Athens and the Pantheon in Rome is an excellent example of the embodiment of classical architecture theory which with a careful and thorough attitude takes into account the principles of order, geometry and its measures, accompanied by the fineness of "craftmanship" art. Need to know that the building is experiencing a long period of construction, from the time of the beginning of construction, revision, repair and completion many times until until the form pad could finally reach more than 200 years. The architectural tradition initiated by Vitruvius has continued in the days of Classical Architecture. This can be found in the Roman Encyclopedia book compiled by Marcus T. Varro, where Isodore from Seville describes and develops the Vitruvius theory in three building elements : Dispositio, Constructio and Venustas.
Dispositio are activities related to field surveys or work on existing sites, floors and foundations. Venustas is associated with elements added to the building to fulfill the desire for a sense of beauty through the art of ornamentation or decoration. This description shows that there is a shift in view of Vitruvius Theory. Furthermore Isodore states what it is the order as follows: "The column, named so because it is tall and round, sustains all the weight existing building load.
The old Ratio or Proportion states that the width is one-third of the height. Known 4 types of columns are: Doric, Ionic, Tuscan and Corinthian, which vary with each other in height and diameter. Type 5, named ATTIC with a square-4 or larger and made of bricks being prepared ". (Isodore in Varro, 19xx).
This Isodore opinion can be a number of rules and norms for later architectural works.
Classical architectural values can also be found in church buildings that are initiating growth and development as a new religion and spreading almost the whole continent of Europe at that time. One such building is the Hagia Sophia depicted in a context urban then as follows: "Thus the building of this Church is trying to give the presentation of that form amazing. Because this building reaches up into the sky until the clouds and so prominent among the other buildings, from the top of this church can see down all corners of the city of Constantinople. The Hagia Sophia is such a form that integrates with the city of Constantinople, but on the other hand it is so radiant and beautiful, and majestic, especially in the perspective of the "Bird Eye View ". And these things are complete and perfect with the use of this building for religious ceremonies "(Isodore in Varro, 19xx).
Classical architectural theory is then continued until the Gothic era. And to absorb and understand the Gothic Architecture is needed a picture of the atmosphere of society at that time where arises the spirit of the soul trying to find the essence of God's divine attributes. Spiritual spirit is poured in a theme
"Divine light in architectural space" (Ven, 1991), this classical Gothic Classical Architectural Space is expressed as an atmospheric visual beauty, such as diaphanitas, density, obscuritas (darkness) or umbria (shadow). This description of the Gothic Architectural space is also expressed as a concept of brightness or silence that can be seen in other forms,
window shapes, especially the form of stained-glass rosette windows (rosetta) or other tin glass artwork.