Hi Steemians! In this article Im gonna talked about Animals that can easily reproduce in their own called parthenogenesis. Enjoy! :)

Source
Virgin Births are nothing extraordinary in nature. Everything considered, not by any extend of the creative ability. Nevertheless, the ability to duplicate without a male taking an interest in arrangement, called parthenogenesis, is more normal than you may might speculate. Shockingly, various species have been known to rehash abiogenetically, and we're not just talking single-celled living things, either. Different plants and even animals can do all things considered. Here are ten of the most enchanting animals that can reproduce without sex.
#1. Snakes.
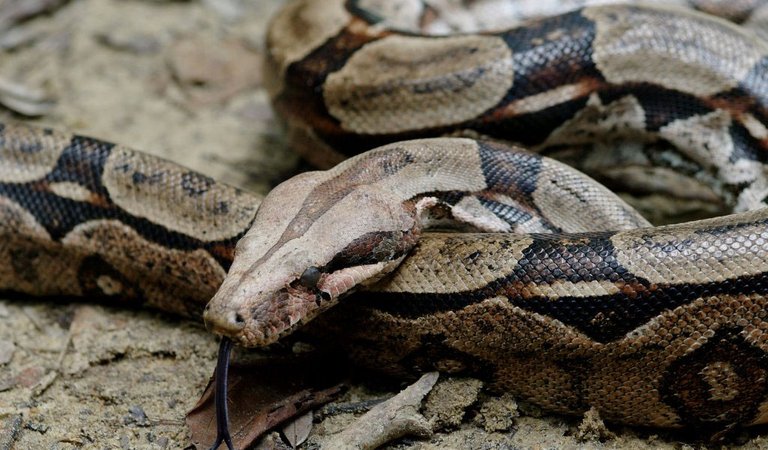

Source
Analysts have found an organic stunner, Female boa constrictors are fit for conceiving an offspring Asexually. Be that as it may, the astonishment doesn't end there. The examination in Biology Letters found that boa babies delivered through this abiogenetic proliferation also called parthenogenesis brandish a chromosomal peculiarity that analysts thought was unthinkable in reptiles.
While specialists concede that the female in the examination may have been a hereditary oddity, they say the discoveries should squeeze analysts to reevaluate reptile propagation. Virgin birth among reptiles, particularly crude ones like boas, they contend might be significantly more typical than anticipated.
"Repeating both ways could be a developmental 'escape imprison free card' for snakes," says lead creator Warren Booth, a North Carolina State University postdoctoral entomologist. "In the event that reasonable males are missing, why squander those costly eggs when you can possibly put out some half-clones of yourself? At that point, when a reasonable mate is accessible, return to sexual propagation."
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
#2. The Cape Honey Bee

Source
There are 20,000 types of Honey bees over the planet yet special case that can reproduce without a requirement for male honey bees. The Cape honey bee, (Apis mellifera capensis) is a South African animal categories equipped for reproducing by means of a procedure called thelytoky. Thelytoky is a type of parthenogenesis that enables working drones to lay diploid, female eggs. The subsequent honey bee will dependably be female and is conceived without the egg waiting be treated.
Just few Cape honey bee specialists express the thelytoky phenotype to recreate abiogenetically, yet they can keep up populace heterozygosity, which implies the recently brought forth honey bees aren't immediate clones of the parent. Rather, they include variation sets of chromosomes, making them new, one of a kind people inside the hive. The honey bees frequently lay eggs when new specialists are required or when it ends up important to incubate another ruler.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
#3. Saw Fish

Source
A critically endangered types of fish in the southeastern United States can reproduce without anyone else. Specialists contemplating a little small tooth Sawfish (otherwise called the woodworker shark) populace in a Florida estuary have discovered that the fish takes an interest in parthenogenesis, a procedure through which females can deliver posterity without the help of a male.
Although in spineless creatures, parthenogenesis is comprehended to be greatly uncommon in vertebrates. Analysts trust that an unfertilized egg can retain an indistinguishable sister cell, despite the fact that the subsequent posterity ordinarily have next to no hereditary decent variety and infrequently get by past birth. Researchers have watched the training in imprisonment, yet this speaks to the principal occasion of parthenogenesis in nature.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
#4. Marbled Crayfish
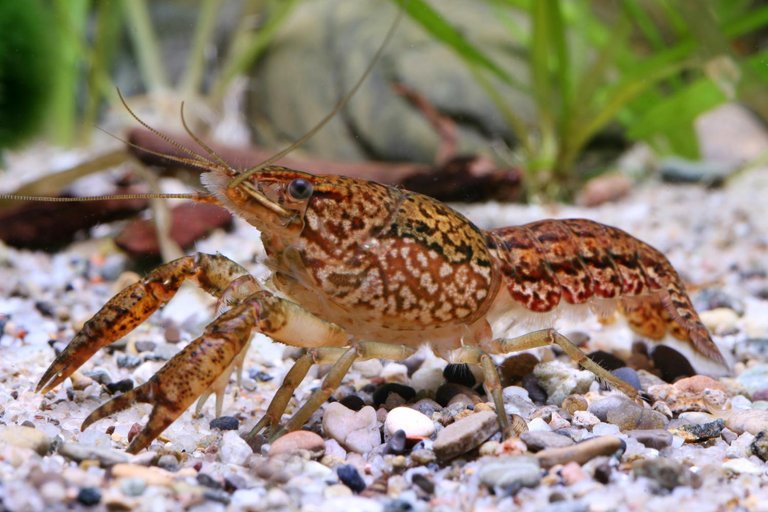

Source
The most fascinating thing about the marbled crawfish isn't that it reproduce itself magically. The species didn't exist until at some point in the late 1990s. It just exists now on account of a solitary transformation in a parent animal groups that brought about the speciation of a fresh out of the box new kind of crawfish. These little critters are somewhat wonderful and have advanced into the pet market in Germany, however that introduced a little issue.
Marbled crawfish clone themselves by the hundreds!A single female marbled crawfish can lay many eggs at one time, so individuals who put one into an aquarium soon end up possessing more than they can deal with. Accordingly, the species has turned out to be obtrusive everywhere throughout the world, with particularly harming impacts in places like Madagascar, where a large number of clones undermine local natural life. They have been contrasted with Star Trek 's tribbles, which imitate wildly, and keeping in mind that they are fascinating, they speak to an unsafe risk to various environments.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
#5. New Mexico Whiptail
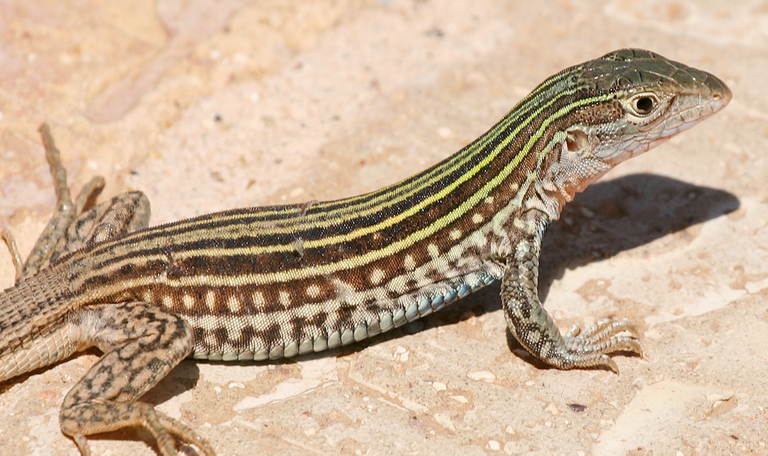

Source
Of the roughly 1,500 known species fit for reproducing through parthenogenesis, most are plants, creepy crawlies, and arthropods. The capacity to reproduce without preparing an egg is uncommon in vertebrate species, yet it has been seen in few reptiles. The New Mexico whiptail is a fascinating illustration in light of the fact that the whole species is totally without guys. New Mexico whiptails are hybridized posterity of two different species where guys are available: the little striped whiptail and the western whiptail.
The hybridization of these reptile species doesn't take into consideration solid male posterity to frame, however that doesn't prevent the New Mexico whiptail from walking alone species, which is even perceived as the state reptile of New Mexico. The female posterity that make up the number of inhabitants in New Mexico whiptails can lay up to four unfertilized eggs in the late spring. These then incubate around two months after the fact into new female individuals from the populace.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
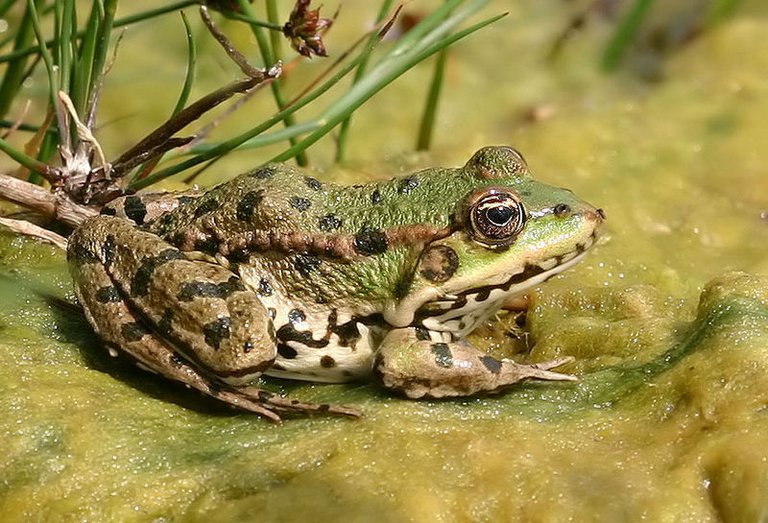
#6. The Edible Frog

Source
The relevantly named edible frog (Pelophylax esculentus) is a typical European types of water or green frog. It is the essential species utilized as a part of France for sustenance, as its legs are fairly top notch when arranged legitimately. These frogs reproduce through a procedure of hybridogenesis, which works in a way like parthenogenesis. Females make hybridogenetic cross breeds, which bar one portion of the parent qualities to make another age of posterity with half of the qualities created clonally and the other half passed sexually.
This procedure of proliferation takes the hereditary material from the father's side and recombines it into something totally new. While this isn't precisely parthenogenesis or abiogenetic generation however a subclass of the procedure, it's on this rundown because of the idea of the posterity. Each ensuing age conveys the mother's DNA while just conveying a hybridized genome of the father. The cutting edge can deliver guys, however their DNA is, it could be said, a clone of their mom's with their dad's recombined into something the mother made for her offspring.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
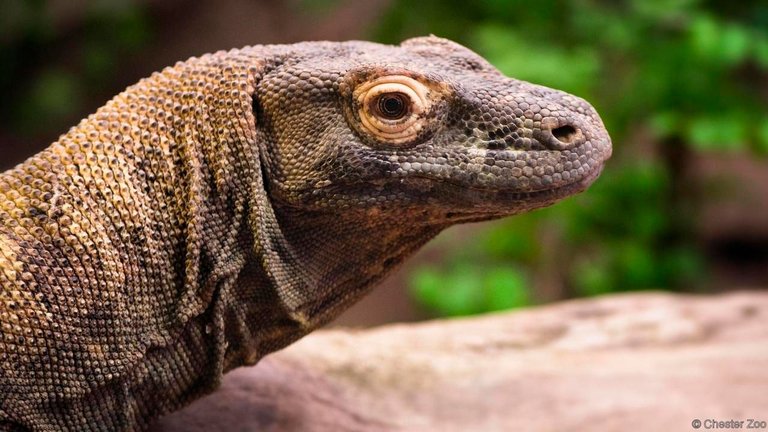
#7. Komodo Dragons

Source
Komodo Dragons have fascinated individuals because of their staggering size and correlation with old reptiles long wiped out from the Earth. They are the biggest living types of reptile and can grow up to 3 meters (10 ft) long and tip the scales at an astounding 70 kilograms (154 lb). They go after expansive creatures like deer and pigs however could presumably take out a human in the event that they felt like it, on account of the poisons contained in their nibbles. These reptiles weren't known to reproduce parthenogenetically until 2005, when an example at the London Zoo laid eggs subsequent to having had no contact with any guys for more than two years. At first, it was suspected that she put away sperm until the point when it was required for utilize, yet this was demonstrated false when hereditary testing affirmed there was no extra hereditary material present.
The same thing has happened to different other female Komodo Dragon in imprisonment everywhere throughout the world. A large number of the eggs that bring forth wind up being male, which is strange for a creature reproducing magically. They achieve this by means of their ZW chromosomal sex-assurance framework, which contrasts from the mammalian arrangement of XY chromosomes. At the point when a Komodo Dragon enters a detached territory like an island (or terrarium), she can create male posterity to mate with. While this isn't something people ought to ever do, for the mythical beasts, it makes a reasonable populace that enables the species to proceed, however it degrades hereditary decent variety.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
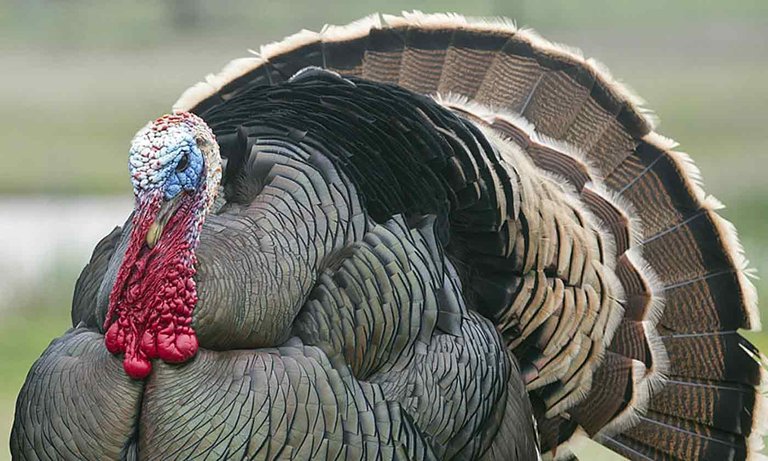
#8. Turkeys

Source
Many people don't care about turkeys, however they eat their meat consistently. Turkeys are fit for duplicating by means of parthenogenesis when females are isolated from a male populace. Strikingly, a female turkey set inside earshot of guys will duplicate magically significantly more regularly than when she is avoided them. The procedure is uncommon in wild turkeys, yet it has been noted to happen in different places and is significantly more typical in trained places in farms.
When an egg hatches without the advantage of a male, it is constantly conceived male. While a female laid the eggs, the male chicks she incubates are largely hereditary clones of her, with the main contrast being the sex. Turkey raisers have observed this and have attempted to compel parthenogenesis in females with the goal that different hereditary characteristics like bigger bosoms are passed down to her posterity.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
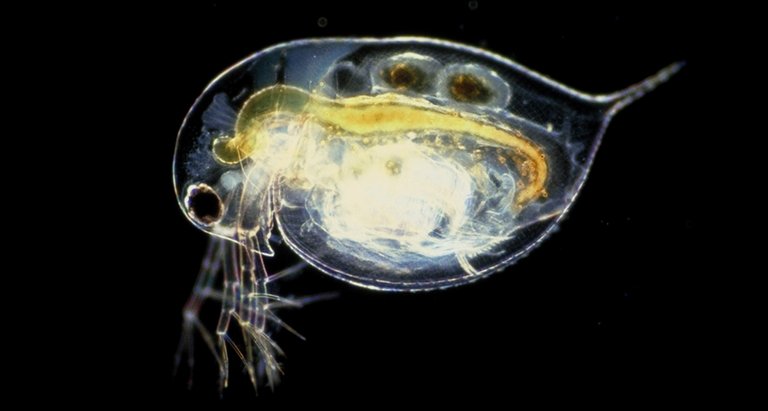
#9. Water Flea
Source
The most well-known types of water flea, Daphnia pulex, found in the waters all through the Americas, Australia, and Europe, holds a couple of remarkable refinements in sea life science. It is a "model animal categories" and was the main scavanger to have its whole genome sequenced. It additionally can reproduce through a procedure called repetitive parthenogenesis, which enables it to interchange between both sexual and abiogenetic reproduction.Observations of Daphnia pulex demonstrate the species will share in recurrent parthenogenesis at whatever point conditions are good in the water.
In the event that an individual happens to get together with an individual from the contrary sex, they get occupied, however in the event that they don't, it doesn't make a difference. A water insect that chooses to make posterity will do as such by creating a hereditarily indistinguishable grip of eggs comprising completely of females. While the hereditary code continues as before, this offers a bigger populace of females to spread those qualities all through the earth, bringing about an exponential development of the general population.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
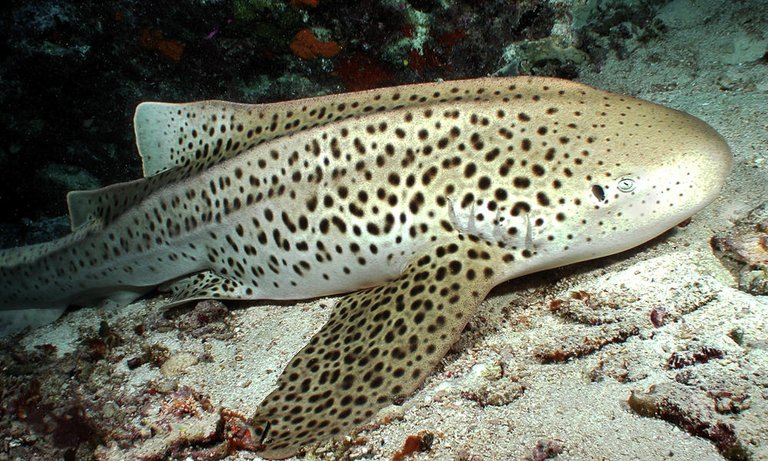
#10.Zebra Shark

Source
It appears the more perplexing the creature, the more improbable it will have the capacity to reproduce magically. Sharks are absolutely mind boggling, however there have been noted cases of zebra sharks reproducing without trying to get any of that bothersome DNA from a male partner. Zebra sharks are tame nighttime angle that have since quite a while ago intrigued people, yet it was just as of late that we watched parthenogenesis in the species.
The first time was with a shark named Leonie, which had been living in an aquarium separated from any guys for quite a while. Following four years of detachment, she laid eggs that delivered three offspring. Since that first perception, other zebra sharks have been appeared to create posterity without a mate. It gives the idea that they can do this paying little mind to their mating conditions. A few examples have been noted to create posterity containing just their hereditary code notwithstanding when within the sight of guys in their environment.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
I hope you enjoyed reading this article. I also ask myself if animals can reproduce without a mate? could humans do the same? I Wonder! :)

I really like the post about animals
This was a fun thing to read! I love all the pics and videos!
Im glad you like it @treeshaface. :)
This is indeed interesting 👍
Im glad you like it. :') i hope you learn something on it. :')
Yes, this is indeed very informative.
interesting! i cnt imagine our numbers if we can self reproduce:)
hahahaha indeed. :D im glad you like it. :)
This article is really interesting! Thank you!
Que interesante!!!! Graciass:D