
SOURCE
Hello friends of the farm in this opportunity I am going to speak to you which are the most recommended conditions for the health of the soils and the most important biological activities. Healthy soils are the foundation of the food system. Our soils are the basis of agriculture and the environment in which almost all plants grown for the production of food grow. Healthy soils produce healthy crops that feed people and animals. In fact, the quality of the soils is directly related to the quality and quantity of food.
The soils provide the essential nutrients, water, oxygen and support for the roots that our plants destined for the production of food need to grow and flourish. In addition, they play a buffer function by protecting the delicate roots of plants from temperature fluctuations.
A healthy soil is a living and dynamic ecosystem, full of microscopic and larger organisms that fulfill many vital functions, including transforming inert and decomposing matter, as well as minerals, into nutrients for plants. In addition, healthy soils contribute to mitigate climate change by maintaining or increasing its carbon content.
Soil health is defined as the continuous capacity of the soil to function as a vital ecosystem that supports plants, animals and humans. As is known, soil is a natural body of great importance that provides environmental services, allows the growth of plants, stores water and retains nutrients, and is a reservoir of organisms such as bacteria, fungi, nematodes, etc. To make the soil work properly, it is important to use road management practices to improve soil health and thereby achieve agronomic benefits (increase productivity and profitability of crops) and environmental, immediate and in the future .
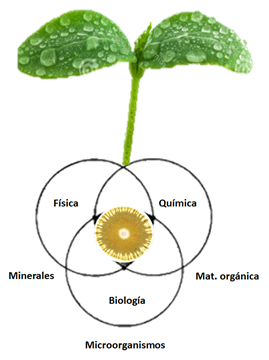
From the agricultural and environmental point of view, soil health is directly related to favorable physical, chemical and biological properties that promote the development of plants and contribute to environmental quality.
SOIL HEALTH WE CAN DIVIDE IN SOIL PHYSICAL HEALTH, SOIL CHEMICAL HEALTH AND SOIL BIOLOGICAL HEALTH;
PHYSICAL HEALTH OF THE SOIL.
This concept is related to the balance that the soil has in conserving and draining water, as well as its capacity not to restrict the growth of the roots of vegetables. The above is related to soil texture, permeability, porosity and drainage, mainly.
SOIL CHEMICAL HEALTH.
It is defined as the capacity of the soil for the nutrients to be in balance and available for the plants. In addition, that the acidity and alkalinity of the soil is in an optimum range for the crop, and that there are no problems of salinity or sodicity.
BIOLOGICAL SOIL HEALTH.
A biologically sound soil is one that has a great activity of living beings that compose it, since it interacts millions of small and large organisms. In the soil we can find populations of fungi, bacteria, nematodes and other organisms. The loading of soil organisms is related to the content of organic matter. In addition, soils with a high amount of microorganisms decompose vegetable waste more easily and quickly, which positively impacts the chemical and physical health of the soil.
Over the years, different soil properties are altered as a result of the use and agricultural management of the soil, where many times poor management can cause some type of degradation. On the other hand, for producers to satisfy the demand for food in view of the growth of the population estimated for the year 2050, agricultural production must increase by 70%. So, how to safeguard soil health and at the same time intensify agricultural activities? Faced with this challenge, farmers must implement good agricultural practices that can rebuild or safeguard soil health.
TO MAINTAIN HEALTH OF THE SOIL IS RECOMMENDED:
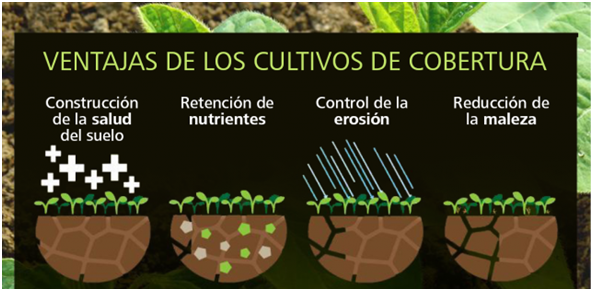
CROPS OF COVERAGE.
Some plant species are recommended as rotation crops when at some time of the year it is not possible to establish the traditional crop due to the weather or because of the incidence of a pest or disease. These crops protect the soil from erosion caused by wind and water, and some of them, such as legumes, fix atmospheric nitrogen.
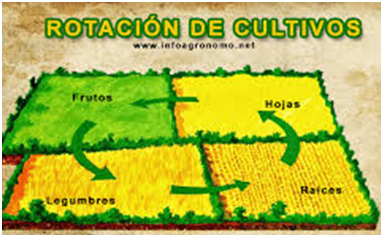
ROTATIONS OF CROPS.
Changing the crop from one year to the next in a field will provide a variety of root systems and different crop residues. This practice can benefit soil organic matter levels.
ADDITION OF ORGANIC AMENDMENTS.
The application of organic material to the soil will gradually increase the level of organic matter. Soils with high levels of organic matter have greater microbial activity, in addition soil resistance is improved, as well as water retention and aeration. Soil health is the continuous capacity of the soil to function as a vital ecosystem that supports plants, animals and humans.
DRAINAGE OF THE SUBSOIL.
In soils that have high water retention capacity (clay), it is common to perform rehabilitation by installing a drainage system. Well-drained soils are healthier and less prone to compaction. In addition, the gas exchange is better (aeration) and the rooting depth is greater.
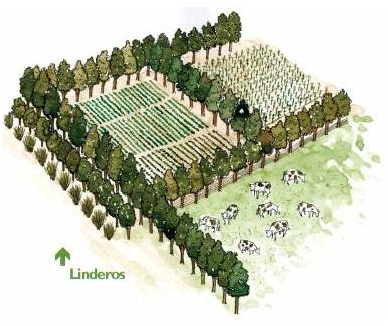
BREAKING BARRIERS.
This type of barriers provides protection against soil erosion, mainly wind. Its function is to reduce the wind speed and avoid the loss of soil.
SOIL ANALYSIS.
A healthy soil is a fertile soil. In this sense, the soil analyzes to know the evolution of nutrient availability in the soil must be done periodically and the fertilization programs adjusted according to the results, as well as the application programs of breeders and organic amendments.
A healthy soil is achieved through the use of appropriate management practices that ultimately impact the productivity and profitability of the crop. Therefore, both scientists and farmers must have a more complete understanding of the state of health of the soil in order to conduct a management plan aimed at improving the resource through holistic, adaptive and data-based approaches.
THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY IN THE SOIL
Soil biota has a very important role in the processes of nutrient recycling and, therefore, in the capacity of a soil to provide the crop with these nutrients. The continuous addition of organic materials to the soil through its transformation by soil organisms, provides the author's capacity to recover the architecture of the soil that has been damaged. Sticky substances on the skin of earthworms and those produced by fungi and bacteria help to agglutinate the particles.
Traces left by earthworms are also more resistant (compacted) aggregates. Organisms and soil microorganism use the residues of plants, animals and derivatives of OM as food. When these decompose waste and organic matter, they release nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur, which the plant can take advantage of. The same activity of microorganisms contributes to the formation of stable organic matter in the soil.
MO AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY
The decomposition of OM is a biological process that occurs naturally. Its speed is determined by the following factors:
Composition and quantity of soil organisms
Physical environment (oxygen, humidity and temperature)
Quality of organic matter
Microorganisms such as bacteria, and invertebrates such as earthworms and insects, help to break down crop residues by ingesting them and mixing them with the mother mineral of the soil; in the process they recycle energy and nutrients from the plants.
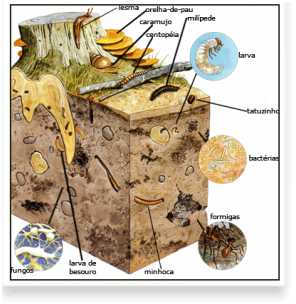
The life in the soil is constituted by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, nematodes, viruses and algae; and macroorganisms in soils include vertebrates and invertebrates. This last group includes arthropods that vary from mites to large beetles, millipedes, termites and earthworms, among others.
The plants, represented by their roots and their residues on the surface of the soil, form the macroflora of the soil. All these elements have their own function in the processes of nutrient recycling.
IMPORTANCE OF BACTERIA
Bacteria decompose easy-to-use substrates, simple carbon compounds such as radical exudates and fresh plant residues. The waste produced by bacteria is converted into organic matter. Some microorganisms can even break down pesticides and contaminants in the soil. They are especially important in the immobilization and retention of nutrients in their cells and, therefore, prevent the loss of nutrients from the root zone.
IMPORTANCE OF THE FUNGI
They break down more resistant organic matter, retaining in the soil the nutrients obtained in the form of fungal biomass and the release of CO2 dioxide. The less resistant material is decomposed first while the more resistant material, such as lignin and proteins, is decomposed in several stages. Many of the secondary waste products are organic acids; therefore, fungi help to increase the accumulation of organic matter rich in humic acids, resistant to further degradation.
IMPORTANCE OF PROTOZOARIES
In agricultural soils, protozoa are the largest producers of the nitrogen available to plants. Between 40-80% of the nitrogen of the plants can come from the predator-prey interaction of protozoa with bacteria. The nitrogen released by the protozoa is in the form of ammonium (NH4 +) and thus easily available to the roots of plants and other organisms.
IMPORTANCE OF NEMATODES
When there are nematodes that feed on bacteria and fungi, nitrogen is released as (NH4 +), making nitrogen available for the growth of plants and other soil organisms.
IMPORTANCE OF THE WORM
They promote microbiological activity by fragmenting OM and increasing the area accessible to fungi and bacteria. In addition, they stimulate the extensive growth of the roots in the subsoil due to the greater availability of nitrogen in the tunnels and the easy penetration of the roots by the existing channels.
IMPORTANCE OF MAINTAINING SOIL ORGANIC MATTER
The organisms depend on their sources of food (which in turn depend on the season) and, therefore, are not uniformly distributed through the soil or uniformly present throughout the year. Each species and group exists where they can find an appropriate supply of food, space, nutrients and moisture. These conditions occur wherever organic matter is present; therefore, soil organisms are concentrated around the roots, in the waste, in the humus, on the surface of the soil aggregates and in the spaces between those aggregates.
IN CONCLUSION:
The availability of food is an important factor that influences the level of activity of soil organisms and, therefore, is related to the use and management of the soil. We can also say that farmers play a key role in this regard the various agricultural approaches promote the sustainable management of soils in order to improve productivity, agroecology, conservation agriculture, organic farming, no-till farming and agroforestry. Finally, a better understanding of the relationships between the useful period of soils and the function of ecosystems and the impact of human interventions will reduce the negative effects and make more effective use of the benefits of the biological activity of soils with look to a more sustainable and productive agriculture.
SOURCE
http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soil-degradation-restoration/evaluacion-de-los-global-indicators-of-the-salud-del-suelo/salud-global-del-suelo/es/
https://www.intagri.com/articulos/suelos/importancia-de-la-materia-organica-en-la-actividad-biologica-en-el-suelo
Thank you for taking a few minutes to read my article.












Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
http://www.fao.org/docrep/009/a0100e/a0100e05.htm
APOLOGIZE BUT THAT THEME THAT YOU ARE MENTIONING HAS NOTHING TO SEE THAT I INVESTIGATE. VERIFY YOURSELF IN THE SOURCES THAT I USE TO INVESTIGATE MY WORK.